Introduction to Industry 4.0
- FutureFactor360
- Sep 30, 2021
- 3 min read
Over the course of manufacturing history, global enterprises have adopted various levers to lower cost, increase productivity, enhance quality & create product differentiation.
Each industrial revolution has enabled a significant jump in each of the above business metrics

How did we get here?
Brief overview of the industrial revolutions thus far
Industry 1.0: Introduced mechanized production capabilities that allowed economic mass production. The focus was on efficiency and scale
Industry 2.0: Led by the advent of machines that ran on electricity. Helped achieve greater production quality and resource utilization
Industry 3.0: Facilitated by advances in the electronics industry. It marked the large-scale adoption of technology and IT systems for the first time. The usage of advanced electronic and automated systems such as PLCs helped automate processes and achieved increased production speed, greater accuracy and lower operating costs
Industry 4.0: A combination of cyber-physical systems and IoT is helping create a virtual, transparent and real-time view of production. Leveraging advanced digital technologies today allows for full automation of manufacturing
What we mean by Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is a name given to the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It encompasses the digitalization of the horizontal and vertical value chain, innovation in products, processes, people practice and creation of new business models
What makes Industry 4.0 different
The fusion of emerging technologies and their interaction across the physical, digital and biological domains make Industry 4.0 fundamentally different from the previous revolutions – diffusing faster and more broadly across various industries and functions.
The disruptive technologies, driven by exponential rise in data volumes, computing power, connectivity and low costs of storage are giving companies the opportunity to adapt their business models to capture new value pools.
I4.0 comprises of below design principles
Evolutionary: The ability to constantly review and adopt pioneering technological innovations
Convergence: Merger of previously separated processes, systems, technologies, business units and solutions
Interoperability: The interconnectedness of devices and systems will require interoperability of the entire infrastructure to reduce integration complexities
Modularity: Modularity approach offers the advantage of transparency allowing much higher levels of decentralized action and decision making
Personalization: I4.0 paves the way for transitioning from mass customization to mass personalization production
Real-time: Availability of intelligence and data insights in real-time enable maximum transparency and better decision making
Virtualization: The merger of physical and digital worlds will give rise to connected system of systems (Cyber-Physical systems)
Servitization: Enables new business models that can be leveraged via connected products to create a more personalized experience for customers
Key growth drivers for Industry 4.0
The rapid global adoption is being driven by key factors such as:
Low cost of computation and storage
Advancements in sensor/ connectivity technology
Ease of integration between disparate systems (through APIs, Data Lakes)
Emergence of analytics and business-intelligence systems
New forms of human machine interfaces
Rise of emerging digital technologies
Reduced Production Costs
I4.0: Levers of Value Creation
Industry 4.0 brings many avenues to create business value, improve productivity and quality.
10-30% reduction in design and engineering costs
20-50% decrease in inventory holding costs
20-50% reduction in time-to-market
10-20% reduction in costs for quality
3-5% increase in overall productivity
45-55% increase of productivity through automation of knowledge work
30-50% reduction of total downtime
85%+ increase in forecasting accuracy
Source: McKinsey Industry 4.0 Global Expert Study
Outlook
Given the current trends and value creation potential, it is certain that Industry 4.0 is not just one of the trending buzzwords.
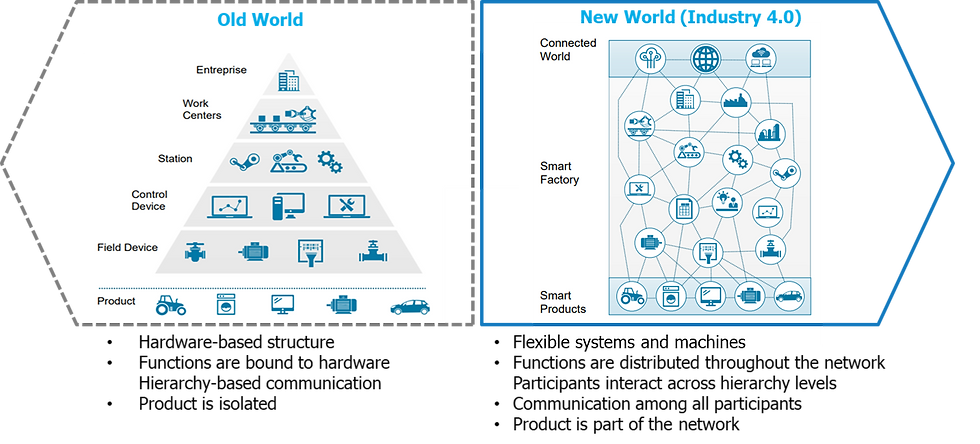
Industry 4.0 will lay the foundations to the future of global businesses as we imagine it today: by enabling a connected, smart, intelligent enterprise
Executives should take Industry 4.0 into consideration as they draft the company’s growth strategy. They must be quick to recognize business opportunities enabled by Industry 4.0 and also watch for peers adopting them.
It is important to acknowledge that Industry 4.0 is not just about making isolated investments through pilots but taking a more holistic approach to digital transformation of the organization across the pillars of people, products, processes and technology.



Comments